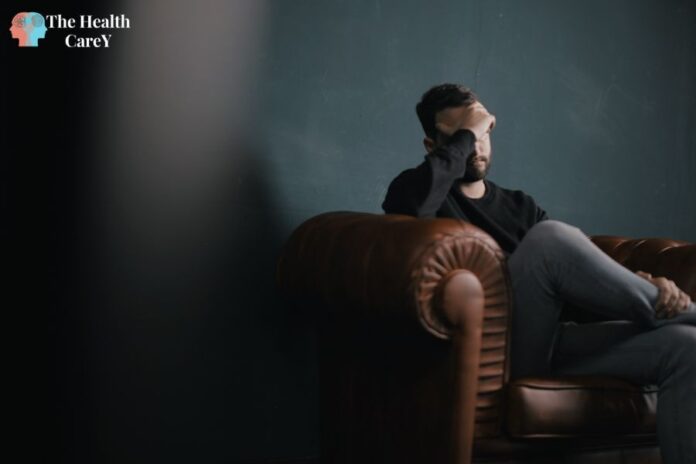
If you or someone you know is struggling with mental illness, the term “relapse” may be familiar. Relapse refers to a return of symptoms after a period of improvement and is a common experience for individuals living with mental health conditions. Whether you are dealing with depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or another mental health issue, understanding what relapse means and how to prevent it can be an important part of your recovery journey.
For many people, the idea of relapse can be scary or overwhelming. It can feel like a setback, or even a failure, to experience a return of symptoms after making progress. However, it’s important to remember that relapse is a normal and expected part of recovery. Just as physical illnesses can recur or flare up, mental health conditions can also be unpredictable and require ongoing management. By learning more about what relapse means and developing a plan to cope with it, you can feel more empowered and in control of your mental health.
What is Relapse?
Relapse is a common occurrence in mental health, especially for those diagnosed with a mental illness. It refers to the return of symptoms or the worsening of a previously improved condition. If you have experienced a relapse, seeking help from a mental health professional is important.
Relapse can happen for a variety of reasons, including:
- Stopping medication or therapy too soon
- Failing to follow a treatment plan
- Exposure to stress or triggers
- Substance abuse
- Changes in physical health
It is important to recognize the warning signs of a relapse, which can include:
- Changes in mood or behavior
- Difficulty sleeping
- Loss of appetite
- Increased anxiety or irritability
- Thoughts of suicide
If you notice any of these warning signs, seeking help from a mental health professional as soon as possible is important.
Relapse does not mean you have failed or your treatment is not working. It is a natural part of the recovery process, and you can get back on track with the right support. Your mental health professional can work with you to develop a new treatment plan or adjust your current plan to help you manage your symptoms and prevent future relapses.
Remember, recovery is a journey, and setbacks are a normal part. With the right help and support, you can overcome relapse and continue on your path to recovery.
What Does Relapse Mean in Mental Health?
Relapse in mental health refers to the return or worsening of symptoms of a mental illness after a period of improvement. It is a common occurrence in mental health conditions and can happen to anyone, regardless of the severity of their illness.
Relapse can be triggered by various factors such as stress, trauma, lack of treatment, or medication changes. It is important to note that relapse does not mean the individual has failed in their recovery journey. It is simply a setback that requires additional support and treatment.
Recognizing the warning signs of relapse is crucial in preventing it from happening. These signs may include a change in sleep patterns, loss of interest in activities, increased anxiety or irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It is important to seek help from a mental health professional if you notice any warning signs.
Treatment for relapse may include therapy, medication adjustments, and lifestyle changes. Working closely with a mental health professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the individual’s specific needs is important.
In summary, relapse in mental health refers to the return or worsening of symptoms of a mental illness after a period of improvement. It is a common occurrence that requires additional support and treatment. Recognizing the warning signs and seeking help from a mental health professional is crucial in preventing and managing relapse.
Causes of Relapse
Relapse is a common occurrence in mental health, and it can happen to anyone. Many factors can contribute to a relapse, including triggers, addiction and substance use, mental health and symptoms, and life events. Understanding these causes can help you to recognize warning signs and take steps to prevent relapse.
Triggers
Triggers are events or situations that can cause you to experience intense emotions or cravings. Triggers can be anything from stress at work to a difficult conversation with a loved one. It’s important to identify your triggers so that you can avoid them or develop coping strategies to deal with them. Some common triggers include:
- Stressful situations
- Negative emotions like sadness, anger, or anxiety
- Social situations involving drugs or alcohol
- Certain people or places that remind you of past drug use
Addiction and Substance Use
Addiction is a chronic disease that can cause you to experience intense cravings and compulsive drug use. Addiction can also increase your risk of relapse. The brain changes that occur with addiction can make it difficult to control your drug use, even when you want to quit. If you have a history of addiction, it’s important to be aware of the signs of relapse and seek help if you feel at risk.
Mental Health and Symptoms
Mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can also increase your risk of relapse. When experiencing symptoms of a mental health condition, it can be difficult to cope with stress and other triggers. Mental health treatment can help you manage your symptoms and reduce your risk of relapse.
Life Events
Life events like loss, trauma, or major changes can also increase your risk of relapse. These events can be challenging to cope with and trigger intense emotions or cravings. It’s important to have a support system and seek help if you’re struggling to cope with a life event.
In conclusion, relapse is a complex issue with many causes. By understanding the factors contributing to relapse, you can take steps to prevent it and stay on the path to recovery. If you’re struggling with addiction or mental health issues, don’t hesitate to seek help from a qualified healthcare professional.
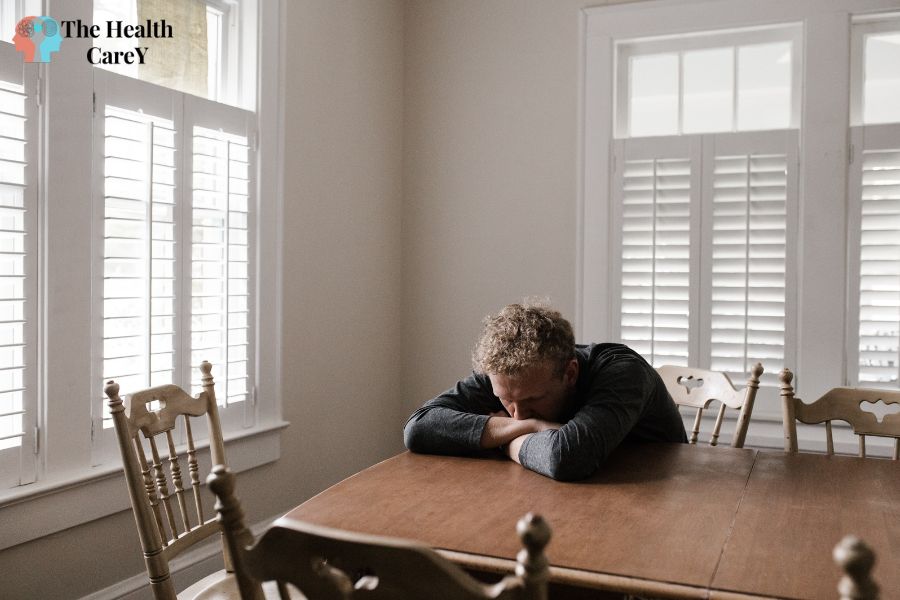

Relapse Prevention Plan
Relapse Prevention Plan: A relapse prevention plan is a proactive strategy to reduce the risk of recurrence or deterioration of mental health symptoms. It involves identifying triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and implementing preventive measures to maintain stability.
Individuals can create personalized plans that address their needs and circumstances by working closely with mental health professionals. This plan serves as a roadmap for navigating potential challenges and staying on track toward recovery.
Support and Therapy:
One of the essential components of relapse prevention is establishing a robust support system. This network can include trusted family members, friends, or support groups who provide understanding, empathy, and encouragement; whether individual or group-based, regular therapy sessions play a pivotal role in maintaining mental well-being.
Therapists can offer valuable insights, teach coping skills, and assist individuals in recognizing early warning signs of relapse. They provide a safe space for exploring emotions, addressing underlying issues, and developing effective strategies for long-term recovery.
Warning Signs and Recurrence
Recognizing the warning signs and understanding the potential for recurrence are crucial aspects of managing mental health and preventing relapse. By familiarizing oneself with these indicators, individuals can take proactive steps to address them effectively. This section explores common warning signs and strategies for managing the risk of recurrence.
Identifying Warning Signs: Warning signs of a potential relapse can vary from person to person and may include changes in behavior, mood, thoughts, or physical symptoms. Examples may include:
- Increased anxiety or irritability.
- Withdrawal from social activities.
- Changes in sleep patterns.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Intrusive negative thoughts.
Individuals must develop self-awareness and recognize these signs as early as possible to take appropriate action.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concept of relapse in mental health is vital for individuals and their support systems. It signifies a recurrence or worsening of mental health symptoms and can significantly affect overall well-being.
By developing a relapse prevention plan, seeking support and therapy, recognizing warning signs, and implementing strategies to manage the risk of recurrence, individuals can empower themselves in their journey towards mental wellness.
It is crucial to remember that each person’s experience is unique, and seeking professional help and maintaining a strong support network are key to navigating the complexities of mental health and fostering long-term recovery.