If you or someone you know has experienced chest pain or discomfort, you may wonder if it’s a heart attack or heart failure. While both conditions involve the heart, they have distinct differences in their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these differences can help you seek appropriate medical care and save a life.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can cause damage to the heart muscle and may even be life-threatening. On the other hand, heart failure is a chronic condition in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body. While heart attack and heart failure are different conditions, they can both be caused by underlying heart disease.
Key Takeaways
- Heart attack and heart failure are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
- A heart attack is caused by a blockage in blood flow to the heart, while heart failure is a chronic condition in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively.
- Understanding the differences between heart attack and heart failure can help you seek appropriate medical care and save a life.
Understanding Heart Attack and Heart Failure
Knowing the difference between heart attack and heart failure is essential if you’re concerned about your health. Both conditions involve the heart, but they are not the same thing.
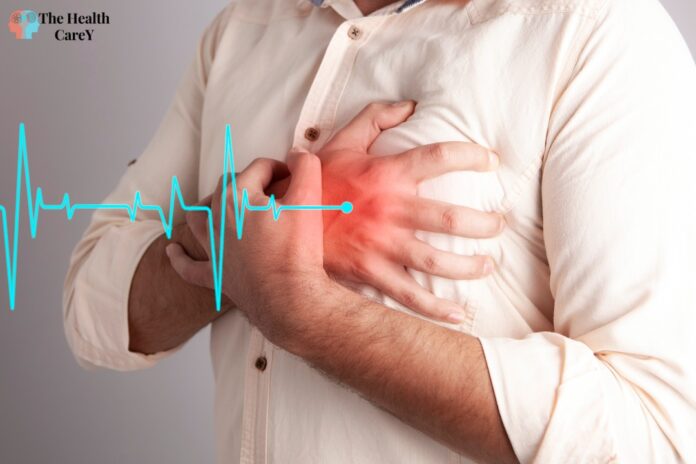
A heart attack, a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can cause damage to the heart muscle and can be life-threatening. Symptoms of a heart attack may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, or discomfort in other upper body areas.
On the other hand, heart failure is when the heart cannot pump blood effectively throughout the body. Various factors, including damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack, high blood pressure, or other underlying health conditions, can cause this. Symptoms of heart failure may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs or ankles, and a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
It’s important to note that heart failure does not mean that the heart has stopped working altogether. Instead, it means that the heart is not working as well as it should be and may need medical intervention to help it function properly.
In summary, a heart attack and heart failure are two different conditions that can affect the heart. While a heart attack is caused by a blockage in blood flow to the heart, heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively. If you are experiencing symptoms of either condition, seeking medical attention immediately is essential.

Causes of Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked, leading to damage or death of heart muscle cells. The most common cause of a heart attack is a blockage in one or more coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. This blockage can be caused by several factors, including:
- Plaque buildup: Over time, fatty deposits called plaque can build up in the walls of the coronary arteries, narrowing the passageway and reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Blood clot: A blood clot can form on the plaque’s surface, further blocking blood flow to the heart muscle.
- High cholesterol: High cholesterol levels in the blood can contribute to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries.
- Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup or other factors.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the lining of the coronary arteries, making it easier for plaque to build up and increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease and other risk factors for heart attack, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to develop coronary artery disease and are at higher risk of having a heart attack.
- Family history: If you have a family history of heart disease, you may be at increased risk of having a heart attack.
- Drug use: Certain drugs, such as cocaine, can cause spasms in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Atherosclerosis: This condition occurs when fatty deposits build up in the walls of arteries throughout the body, including the coronary arteries.
Causes of Heart Failure
Heart failure can occur due to various conditions that affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Here are some of the most common causes of heart failure:
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a leading cause of heart failure. When your blood pressure is too high, it puts extra strain on your heart, which can weaken it over time.
- Coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrow or blocked, which can cause a heart attack. Over time, this condition can also lead to heart failure.
- Heart disease: Various forms of heart disease, such as cardiomyopathy, can cause the heart muscle to become weak and unable to pump blood effectively, leading to heart failure.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart, leading to heart failure.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on the heart, which can lead to heart failure.
- Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can damage the heart muscle and lead to heart failure.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, leading to heart failure.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as viral infections, can cause inflammation in the heart muscle, leading to heart failure.
- Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, which can lead to heart disease and heart failure.
It’s important to note that heart failure can also occur due to other conditions, such as heart valve problems or congenital heart defects. If you have any risk factors for heart failure, taking steps to manage them and reduce your risk is essential.
Symptoms of Heart Attack
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it could be a sign of a heart attack:
- Chest pain or discomfort that feels like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain. This pain can last a few minutes or come and go.
- Shortness of breath, which can occur with or without chest pain.
- Nausea or vomiting, which can be accompanied by cold sweat.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Indigestion or heartburn-like feeling.
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations.
Chest pain is the most common symptom of a heart attack. It can feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain. The discomfort can be mild or severe, lasting more than a few minutes or coming and going. It may also spread to your arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back.
Shortness of breath can occur with or without chest pain. You may feel like you’re running out of breath or can’t catch your breath. You may also feel like you’re suffocating or drowning.
Nausea, vomiting, and cold sweat are other common heart attack symptoms. You may feel like you’re going to throw up or pass out. You may also break out in a cold sweat, even if you’re not doing anything strenuous.
Lightheadedness or dizziness can occur with or without chest pain. You may feel like you’re about to faint or lose consciousness.
Indigestion or heartburn-like feeling can occur with or without chest pain. You may feel like you have an upset stomach or acid reflux.
Irregular heartbeat or palpitations can occur with or without chest pain. You may feel like your heart is racing, fluttering, or skipping a beat.
Remember, not everyone experiences the same symptoms during a heart attack. Some people may have no symptoms, while others may have mild or severe symptoms. If you experience any of these symptoms, call 911 or your local emergency number immediately.
Symptoms of Heart Failure
If you are experiencing heart failure, you may notice a range of symptoms. These symptoms can vary in severity, and you may not experience all of them. Here are some of the most common symptoms of heart failure:
- Shortness of breath: You may feel out of breath even when not exerting yourself. You may also find it difficult to breathe when you lie down.
- Fatigue: You may feel tired and weak, even if you have not been doing anything strenuous.
- Swelling: You may experience swelling in your legs, ankles, and feet. This is due to fluid buildup when your heart is not pumping blood effectively.
- Cough: You may have a persistent cough that produces white or pink mucus.
- Weight gain: You may gain weight rapidly due to fluid buildup.
- Trouble concentrating: You may find it difficult to focus or concentrate, as your brain may not receive enough oxygen.
- Wheezing: You may hear a whistling sound when you breathe due to fluid buildup in your lungs.
- Lack of appetite: You may lose your appetite and feel nauseous.
- Difficulty breathing: You may feel like you are suffocating or drowning, as your lungs may not receive enough oxygen.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, seeking medical attention immediately is vital. Your doctor can help you manage your symptoms and prevent further damage to your heart.
Diagnosis and Tests of Heart Attack or Heart Failure
If you suspect you may be experiencing a heart attack or heart failure, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare provider will perform a physical exam and may order several tests to make a diagnosis.
One of the primary tests used to diagnose a heart attack is an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This test records electrical signals as they travel through your heart and can detect abnormalities in your heart’s rhythm. Blood tests may also be ordered to check for elevated enzyme levels released into the bloodstream during a heart attack.
A healthcare provider may order a chest X-ray to diagnose heart failure to check for an enlarged heart or fluid buildup in the lungs. Blood tests may also be ordered to check for elevated levels of a protein called B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), produced by the heart and can indicate heart failure.
In addition to these tests, your healthcare provider may also check your blood pressure to determine if it is elevated, which can be a risk factor for heart attack and heart failure.
It is important to note that the American Heart Association recommends that all adults have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years. You may need to check your blood pressure more frequently if you have a family history of heart disease or other risk factors, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Remember, if you are experiencing heart attack or heart failure symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to severe complications or even death.
Treatment for Heart Attack
If you are having a heart attack, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Quick treatment can help prevent or minimize heart damage and save your life.
The treatment for a heart attack may include:
- Oxygen therapy: You may receive oxygen through a mask or nasal cannula to help you breathe easier and increase oxygen levels in your blood.
- Nitroglycerin: This medication can help widen your blood vessels and improve blood flow to your heart. It may be given as a tablet to dissolve under your tongue or as a spray.
- Aspirin: Chewing aspirin can help prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of further heart damage.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): This procedure involves inserting a catheter with a balloon at the end into the blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent may be placed to keep the artery open.
- Surgery: In some cases, bypass surgery may be necessary to reroute blood flow around a blocked artery.
Your doctor will determine your best treatment plan based on your needs and medical history. It is essential to follow your doctor’s instructions and take any medications as prescribed to help prevent future heart problems.
Remember, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial in the event of a heart attack. Do not hesitate to call 911 or go to the emergency room if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness.
Treatment for Heart Failure
If you have been diagnosed with heart failure, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on the severity of your condition. Treatment for heart failure typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help manage heart failure symptoms and improve overall health. Your doctor may recommend:
- Dietary changes: A heart-healthy diet low in salt and saturated fats can help manage heart failure symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve heart function and reduce symptoms of heart failure. Your doctor may recommend a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you increase your activity level safely.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can help improve heart function and reduce your risk of further heart damage.
- Weight management: Losing weight can help reduce the workload on your heart and improve heart function.
Medications
Several medications can help manage heart failure symptoms and improve heart function. Your doctor may prescribe:
- ACE inhibitors: These medications help relax blood vessels and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Beta-blockers: These medications help slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure.
- Diuretics: These medications help reduce fluid buildup in the body, improving breathing and reducing swelling.
- Aldosterone antagonists: These medications help reduce fluid buildup and improve heart function.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat heart failure. Your doctor may recommend:
- Coronary bypass surgery: This surgery can improve blood flow to the heart and reduce symptoms of heart failure.
- Heart valve surgery can repair or replace damaged valves, improving heart function.
- Pacemaker or defibrillator: These devices can help regulate heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
- Heart transplant: In severe cases of heart failure, a heart transplant may be necessary to improve heart function and quality of life.
Heart failure treatment aims to improve heart function, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life. With the right treatment plan, many people with heart failure can manage their condition and live full, active lives.
Prevention and Risk Factors
When it comes to heart health, prevention is vital. Understanding the risk factors contributing to heart disease can reduce your risk and maintain a healthy heart.
One of the most significant risk factors for heart disease is age. As you get older, your risk of developing heart disease increases. Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 are at higher risk of heart disease than younger individuals.
However, age is not the only risk factor for heart disease. Lifestyle factors like smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise can also contribute to heart disease. If you smoke, quitting is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your risk of heart disease. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise and a healthy diet into your lifestyle can help reduce your risk.
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are also significant risk factors for heart disease. These conditions can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, increasing your risk of heart attack and stroke. If you have high blood pressure or cholesterol, working with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce your risk of heart disease is essential.
Reducing your risk of heart disease requires lifestyle changes and medical management. By quitting smoking, incorporating regular exercise and a healthy diet into your routine, and managing conditions such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, you can maintain a healthy heart and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Types of Heart Failure
When it comes to heart failure, there are different types that you should be aware of. Some of the most common types of heart failure include:
- Left-sided heart failure is the most common type of heart failure and occurs when the left ventricle of the heart cannot pump enough blood to the body.
- Right-sided heart failure occurs when the heart’s right ventricle cannot pump enough blood to the lungs.
- Systolic heart failure occurs when the heart’s left ventricle cannot contract properly, which means it cannot pump enough blood to the body.
- Diastolic heart failure: This type of heart failure occurs when the left ventricle of the heart cannot relax properly, which means it cannot fill with enough blood to pump to the body.
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): This type of heart failure occurs when the heart’s left ventricle cannot pump blood out properly, reducing the amount of blood pumped out with each heartbeat.
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): This type of heart failure occurs when the heart’s left ventricle cannot relax properly, reducing the amount of blood pumped out with each heartbeat.
It is important to note that various factors, including high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and heart valve problems, can cause heart failure. If you are experiencing symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet, it is crucial to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of heart failure?
Heart failure symptoms may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, rapid or irregular heartbeat, persistent cough or wheezing, nausea or loss of appetite, and difficulty concentrating.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
Heart attack symptoms may include chest pain or discomfort, upper body discomfort, shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea or lightheadedness.
How is heart failure diagnosed?
Heart failure is diagnosed through a physical exam, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, chest X-ray, blood tests, and stress tests.
How is a heart attack diagnosed?
A heart attack is diagnosed through a physical exam, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and imaging tests such as a coronary angiogram or CT scan.
Can heart failure lead to a heart attack?
While heart failure and heart attack are two separate conditions, they can be related. Heart failure can weaken the heart and increase the risk of a heart attack.
What are the differences in causes between heart failure and a heart attack?
Heart failure is often caused by underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and diabetes. A heart attack is caused by a coronary artery blockage that supplies blood to the heart muscle.
Also Read:
Can Dehydration Cause Heart Palpitations?
Causes of Headaches and Heart Palpitations