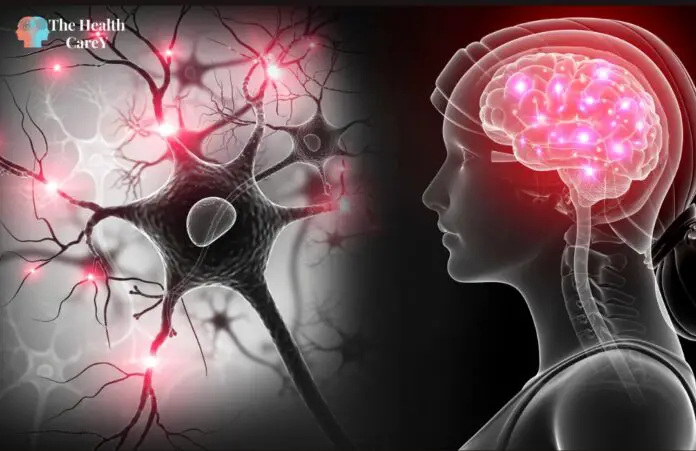
When you think about your health, you might not consider the health of your nervous system. However, your nervous system regulates your body’s functions and responses. When your nervous system becomes dysregulated, it can significantly impact your mental and physical health.
A dysregulated nervous system can manifest in many ways, including feeling shut down, sluggish, or agitated. It can result from trauma or chronic stress and can affect your ability to regulate emotions and responses. Understanding the nervous system and how it functions can help you identify dysregulation and take steps to support your nervous system’s health.
Key Takeaways
- A dysregulated nervous system can significantly impact your mental and physical health.
- Understanding the nervous system can help identify dysregulation and support nervous system health.
- Regulating the nervous system can involve various techniques and lifestyle factors.
Understanding the Nervous System
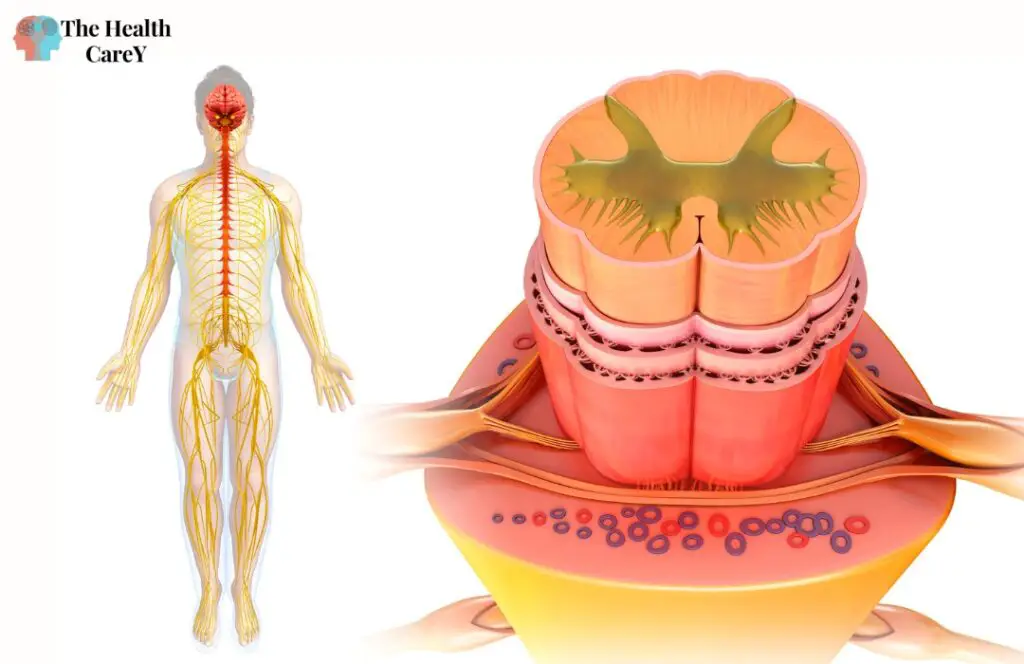
The nervous system is a complex and sophisticated system that regulates and coordinates body activities. It is divided into two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and integrating sensory information, initiating motor responses, and controlling the body’s functions. Conversely, the PNS includes all the nerves outside the CNS that connect the body to the brain and spinal cord.
The nervous system’s basic structural and functional unit is the neuron, a specialized cell that transmits electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. Neurons are connected through synapses, which allow for the transfer of information between cells.
The spinal cord is a long, tubular structure that runs from the brainstem to the lower back. It relays information between the brain and the rest of the body and coordinates reflex responses.
Nervous system dysregulation occurs when there is an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system. This can present as insomnia, migraines, anxiety, chronic pain, GI distress, and high or low blood pressure. A dysregulated nervous system can also manifest as appearing shut down, lazy, or “out of it” as part of the “freeze” or “fawn” trauma responses.
Understanding the nervous system is crucial for recognizing and addressing nervous system dysregulation. By learning about the structure and function of the nervous system, you can better understand how it affects your overall health and well-being.
Dysregulated Nervous System
You may have a dysregulated nervous system if you’re feeling out of sorts, anxious, or lethargic. This imbalance between your autonomic nervous system’s sympathetic and parasympathetic branches can wreak havoc on your physical and mental health. In this section, we’ll explore the causes of dysregulation and the signs and symptoms to watch out for.
Causes of Dysregulation
A dysregulated nervous system can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic stress, trauma, and adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Childhood trauma, in particular, can lead to long-lasting changes in how your nervous system responds to stress. Overstimulation can also lead to dysregulation, hormonal imbalances, high blood pressure, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Signs and Symptoms
When your nervous system is dysregulated, you may experience various physical and emotional symptoms. These can include:
- Insomnia
- Migraines
- Anxiety
- Chronic pain
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- High or low blood pressure
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Difficulty concentrating
You might also find that everyday stressors more easily trigger you and that your reactions are more robust than they should be. You may feel like you’re constantly on edge or unable to relax and unwind.
It’s important to note that dysregulation can manifest differently in different people. Some individuals may experience more physical symptoms, while others may experience more emotional symptoms. If you’re concerned about dealing with a dysregulated nervous system, it’s important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can help you identify the underlying causes of your dysregulation and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a peripheral nervous system (PNS) subcomponent that regulates involuntary physiologic processes, including blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal. It comprises three anatomically distinct divisions: the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous systems. These three systems work together to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response. When activated, it increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration and releases stress hormones like cortisol. This response is designed to help you respond to perceived threats, whether physical or emotional. However, chronic activation of the SNS can lead to health problems like elevated heart rate and blood pressure and an increased risk of heart disease.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is responsible for the body’s “rest and digest” response. When activated, it slows heart rate and respiration, promoting digestion and relaxation. This response is designed to help your body recover and repair itself after periods of stress. Chronic activation of the PSNS can lead to problems like low blood pressure and digestive issues.
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve is a vital part of the parasympathetic nervous system. It regulates heart rate, digestion, and other involuntary processes. Stimulating the vagus nerve can help activate the PSNS and promote relaxation and healing. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help boost the vagus nerve and encourage relaxation.
The autonomic nervous system regulates many essential bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work together to maintain balance in the body, but chronic activation of either system can lead to health problems. Stimulating the vagus nerve can help activate the PSNS and promote relaxation and healing.
Impact of Dysregulation on Mental Health
When your nervous system is dysregulated, it can significantly impact your mental health. Emotional dysregulation is a common symptom of nervous system dysregulation, leading to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty managing emotions. You may feel like you are always on edge, and small things can trigger an intense emotional response.
Hypervigilance is another common symptom of nervous system dysregulation, making it difficult to relax and feel safe. You may feel like you are always on guard, waiting for something terrible to happen. This can lead to constant anxiety and stress, which can take a toll on your mental health over time.
Lying may also become a coping mechanism when you have a dysregulated nervous system. You may feel like you need to hide your true feelings or thoughts to avoid conflict or protect yourself. This can lead to a breakdown in trust in your relationships and further exacerbate your emotional dysregulation.
Poor memory and concentration can also result from a dysregulated nervous system. When your body is constantly stressed, it can be challenging to focus and retain information. This can lead to difficulties at work or school, further contributing to stress and emotional dysregulation.
Burnout is another potential consequence of a dysregulated nervous system. When your body is constantly stressed, it can lead to exhaustion and a lack of motivation. You may feel like you are always running on empty, making managing your daily responsibilities and mental health complex.
Overall, a dysregulated nervous system can significantly impact your mental health and well-being. It is essential to seek help if you are experiencing symptoms of nervous system dysregulation, as many effective treatments are available to help you restore your body’s natural stress response and achieve homeostasis.
Physical Effects of Nervous System Dysregulation
When your nervous system is dysregulated, it can lead to a range of physical symptoms. These symptoms can vary from person to person, but some of the most common physical effects of nervous system dysregulation include:
- Chronic Pain: A dysregulated nervous system can cause chronic pain. This pain may be diffuse or localized and can be challenging to manage with traditional pain medications.
- Panic: Nervous system dysregulation can cause feelings of panic, which can be intense and overwhelming. Various stimuli, including social situations, public speaking, and everyday activities, can trigger these feelings.
- Exhaustion: If your nervous system is dysregulated, you may experience extreme fatigue and exhaustion. This can make it challenging to complete even simple tasks and interfere with your ability to work or socialize.
- Sweating: Sweating is a common physical symptom of nervous system dysregulation. This can be particularly problematic if you experience excessive sweating, which can be embarrassing and interfere with your daily life.
- Insomnia: Nervous system dysregulation can make falling or staying asleep difficult. This can lead to chronic insomnia, which can have a range of adverse effects on your physical and mental health.
- Inflammation: A dysregulated nervous system can cause inflammation throughout your body. This inflammation can lead to a range of health problems, including autoimmune disorders, chronic pain, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a condition that is closely linked to nervous system dysregulation. This condition is characterized by chronic pain, fatigue, and other physical symptoms.
- Sleep Disturbances: Nervous system dysregulation can cause various sleep disturbances, including nightmares, night terrors, and sleepwalking. These disturbances can interfere with your ability to get restful sleep and can lead to chronic fatigue and exhaustion.
- Nausea: Nervous system dysregulation can cause feelings of nausea, which can be particularly problematic if you experience this symptom frequently. This can interfere with your eating ability and lead to malnutrition and other health problems.
Overall, nervous system dysregulation can significantly impact your physical health. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Regulating the Nervous System
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a dysregulated nervous system, there are several ways you can regulate your nervous system. Here are some effective techniques to try.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices can help regulate the nervous system by promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Try incorporating mindfulness techniques into your daily routine, such as focusing on your breath or body sensations and practicing meditation regularly.
Breathing Techniques
Breathing techniques are a simple and effective way to regulate your nervous system. Deep breathing exercises can stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps to calm the body and reduce stress. Try inhaling for four counts, holding for seven counts, and exhaling for eight. Repeat this cycle for a few minutes.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Physical activity and exercise can help regulate the nervous system by increasing blood flow, releasing endorphins, improving mood, and reducing stress. Try incorporating regular movement into your routine, such as yoga or walking.
Diet and Supplements
Diet and supplements can also play a role in regulating the nervous system. Magnesium is a mineral that can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Try incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet, such as spinach and almonds, or a magnesium supplement.
Remember that regulating the nervous system takes time and practice. Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can help promote relaxation and reduce symptoms of a dysregulated nervous system.
Support and Healing
If you are struggling with a dysregulated nervous system, know there are many ways to find support and healing. The journey may not be easy, but you can find relief and recovery with the right tools and guidance.
One of the most important things you can do is seek a therapist or guide specializing in working with the nervous system. They can help you understand the root causes of your dysregulation and provide you with personalized practices and exercises to help you regulate your nervous system.
In addition to working with a therapist, many other practices and techniques can support your healing journey. These may include:
- Mindfulness meditation: This practice can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions, allowing you to respond to them in a more regulated way.
- Yoga: Gentle yoga poses, breathing exercises, and meditation can all help regulate the nervous system and reduce stress.
- Connection with others: Building strong relationships with loved ones and participating in support groups can provide a sense of connection and safety, which can be especially helpful for those who have experienced trauma.
- Touch therapy: Massage, acupuncture, and other forms of touch therapy can help regulate the nervous system and reduce stress.
Remember, healing from a dysregulated nervous system is a journey, and it may take time and patience to find the right combination of practices and support that work for you. But with the right tools and guidance, you can find relief and begin to live a more regulated and fulfilling life.
Research and Theories
Research has shown that a dysregulated nervous system can significantly impact an individual’s physical and mental health. Theories such as the Polyvagal Theory have been developed to explain the mechanisms behind nervous system dysregulation.
Polyvagal Theory
Polyvagal Theory, developed by Dr. Stephen Porges, proposes that the autonomic nervous system has three branches, each with a different role in regulating the body’s response to stress. The ventral vagal branch is responsible for social engagement and relaxation, while the sympathetic and dorsal vagal branches are responsible for fight-or-flight and freeze responses.
According to Polyvagal Theory, when an individual experiences trauma or stress, their nervous system may become dysregulated, leading to hyperarousal or hyperarousal. This dysregulation can result in various symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, and autonomic dysfunction.
Research has shown that practices such as mindfulness and meditation can help regulate the nervous system and improve heart rate variability, a measure of the autonomic nervous system’s flexibility. Additionally, interventions that target the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and exposure therapy, are effective in treating conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder.
In conclusion, understanding the research and theories behind nervous system dysregulation can help individuals better understand their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. The Polyvagal Theory provides a framework for understanding the mechanisms behind nervous system dysregulation and may inform the development of effective interventions.
Lifestyle Factors and Dysregulation
Lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in developing and managing a dysregulated nervous system. Understanding how various aspects of life impact this delicate balance is essential.
1. Stress and Nervous System Dysregulation
Chronic stress can trigger overactive responses in the nervous system, leading to symptoms like anxiety and sleep disturbances. Managing stress through techniques like meditation and relaxation is crucial.
2. Nutrition and Its Impact
*Diet significantly influences nervous system function. Poor dietary choices can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, while a balanced diet supports nervous system health.
3. Sleep Patterns and Nervous System Health
*Healthy sleep patterns are vital. Irregular sleep can disrupt neurotransmitter regulation, affecting mood and cognitive function. Prioritizing quality sleep is critical.
4. Physical Activity and Nervous System Balance
*Regular exercise boosts endorphin release and neuroplasticity, benefiting the nervous system. However, balancing activity and rest is essential to prevent overstimulation.
5. Substance Use and Nervous System Dysregulation
Substance use, including alcohol and drugs, can directly affect the nervous system, leading to imbalances and damage. Seeking help for addiction and substance abuse is crucial for nervous system recovery.
Positive lifestyle changes, such as stress management, a balanced diet, healthy sleep, and responsible substance use, can significantly impact nervous system health, mitigating dysregulation and its associated symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to a dysregulated nervous system:
Q1.What are some physical symptoms of a dysregulated nervous system?
Ans: Physical symptoms of a dysregulated nervous system can include anxiety, panic attacks, muscle tension, tremors, palpitations, digestive problems, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms often result from an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system.
Q2. Can medication help regulate a dysregulated nervous system?
Ans: Medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms of a dysregulated nervous system, such as anxiety or depression. However, they do not address the underlying causes of nervous system dysregulation and are typically used with other therapies like counseling or lifestyle modifications.
Q3. How does a dysregulated nervous system relate to ADHD?
Ans: There is a connection between a dysregulated nervous system and ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). Some individuals with ADHD may have underlying nervous system dysregulation contributing to their symptoms. However, ADHD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder with multiple factors involved, and not all cases are directly related to nervous system dysregulation.
Q4. What is the connection between a dysregulated nervous system and autism?
Ans: Research suggests that there may be a link between a dysregulated nervous system and certain traits associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). People with ASD may exhibit sensory sensitivities and difficulties regulating their nervous system responses to sensory stimuli. However, the relationship between nervous system dysregulation and ASD remains an area of active investigation.
Q5. Are there any recommended books on healing a dysregulated nervous system?
Ans: Some recommended books on healing a dysregulated nervous system include “The Body Keeps the Score” by Bessel van der Kolk, “The Polyvagal Theory” by Stephen Porges, and “Waking the Tiger” by Peter A. Levine. These books provide insights into understanding and healing the nervous system through various approaches.
Q6. What are some signs that indicate a dysregulated nervous system?
Ans: Signs of a dysregulated nervous system can manifest as chronic stress, anxiety, depression, mood swings, insomnia, digestive issues, chronic pain, and hypersensitivity to sensory stimuli. Individuals experiencing these symptoms may benefit from seeking professional evaluation and support for nervous system regulation.