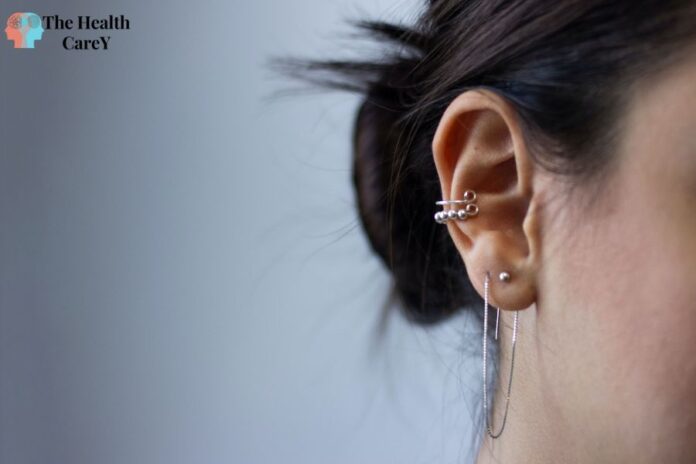
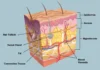
Piercing Bump vs Keloid. You may have noticed a small bump forming around the site if you’ve recently gotten a piercing. While this can be a normal part of the healing process, it’s important to understand the difference between a Piercing Bump vs Keloid. Both can be unsightly and uncomfortable, but they require different treatments.
A piercing bump is a small, raised bump that can form around a piercing. It’s usually caused by irritation or infection and can be easily treated with proper aftercare. On the other hand, a keloid is a thick, raised scar that forms around a piercing and can be difficult to treat. Knowing the difference between the two is important so you can take the appropriate steps to manage the bump and prevent further complications.
What is Piercing Bumps?
You may have noticed a small bump forming near the piercing site if you recently got a piercing. These bumps are called piercing bumps, and they are a common occurrence. This section will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of piercing bumps.
Causes of Piercing Bumps
Piercing bumps can form for a variety of reasons, including:
- Infection: If bacteria or other pathogens enter the piercing site, it can cause an infection, leading to a bump formation.
- Allergic reaction: Some people may be allergic to certain metals used in piercings, such as nickel. An allergic reaction can cause a bump to form.
- Trauma: If the piercing is bumped or knocked, it can cause a bump to form.
- Improper aftercare: If the piercing is not properly cleaned and cared for, it can become infected, forming a bump.
Symptoms of Piercing Bumps
Piercing bumps can vary in size and appearance, but some common symptoms include:
- A small, raised bump near the piercing site
- Redness and swelling around the bump
- Pain or tenderness when touching the bump
- Discharge or pus from the piercing site
Treatment of Piercing Bumps
The treatment for piercing bumps will depend on the cause and severity of the bump. Some common treatments include:
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the bump can help reduce swelling and encourage drainage.
- Saline solution: Cleaning the piercing site with a saline solution can help reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
- Avoiding irritants: If the bump is caused by an allergic reaction, avoiding the irritant (such as a certain metal) can help the bump go away.
- Antibiotics: If an infection causes a bump, antibiotics may be necessary to clear the infection.
P piercing bumps can take time to heal, and it is important to be patient and consistent with your aftercare routine. If the bump does not improve or worsens, seeking medical attention is important.
What is Keloids?
Keloids are raised scars that result from trauma or injury to the skin. They can develop after a piercing, surgery, or any other skin injury. Keloids can be unsightly and uncomfortable and can also cause emotional distress for those with them.
Causes of Keloids
The exact cause of keloids is not known. However, some factors that may increase the risk of developing keloids include:
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing keloids due to their genes.
- Skin type: People with darker skin tones are likelier to develop keloids.
- Age: Keloids are more common in people between 10 and 30.
- Injury: Any injury to the skin, including piercings, can increase the risk of developing keloids.
Symptoms of Keloids
Keloids are characterized by a raised, thickened scar extending beyond the original wound’s boundaries. They may be pink, red, brown, or itchy or painful. In some cases, keloids may also cause:
- Tenderness or discomfort
- Burning or itching
- Changes in the texture or color of the skin
Treatment of Keloids
There are several treatment options available for keloids, including:
- Corticosteroid injections: These injections can help to reduce the size and appearance of keloids.
- Surgery: Surgery can be used to remove keloids but may also cause new keloids to form.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the keloid with liquid nitrogen to reduce its size.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy can reduce the size and appearance of keloids.
It is important to note that keloids can be difficult to treat, and no treatment is guaranteed to be completely effective. It is also important to seek treatment from a qualified healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and effective.
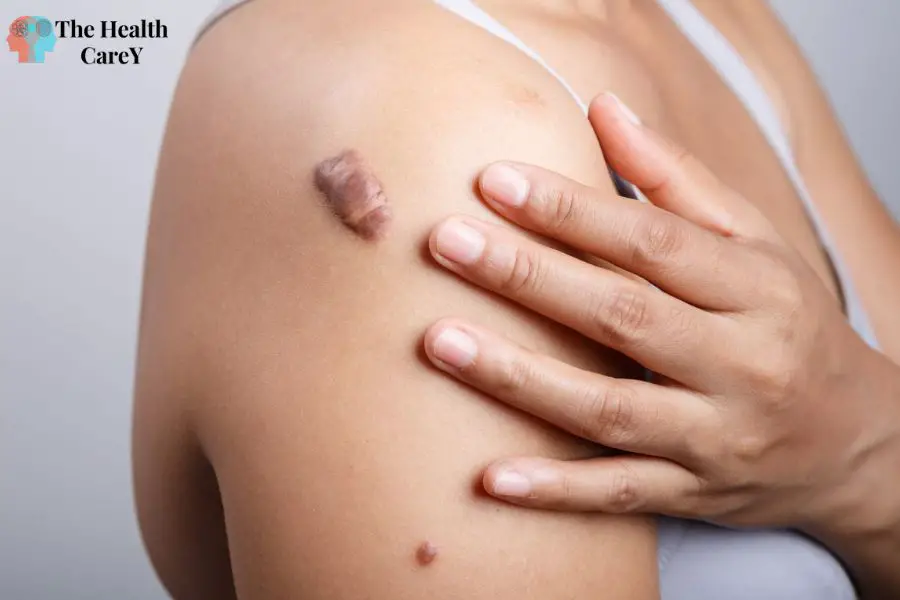
Piercing Bump vs Keloid: Key Differences
When distinguishing a piercing bump from a keloid, there are a few key differences to look out for. While both types of scar tissue can form after a skin injury, there are distinct variations in how they look, feel, and develop.
Appearance
A piercing bump is typically a small, raised bump around the piercing site. It can be red, pink, or flesh-colored and may be accompanied by discharge or tenderness. In contrast, keloids are larger and more irregularly shaped. They can grow beyond the boundaries of the original wound and become thick, raised, and shiny.
Texture
Piercing bumps are usually soft and may feel like a pimple or blister. Keloids, conversely, are firm and rubbery and may be difficult to touch.
Growth
Piercing bumps are self-limiting and may go away independently with proper care. Keloids, however, can continue to grow and expand over time, even beyond the boundaries of the original wound.
Causes
Piercing bumps are often caused by irritation or trauma to the piercing site, while keloids result from an overproduction of collagen during the healing process. Keloids may also be more likely to occur in people with a family history of keloid scarring.
Treatment
Treatment for piercing bumps typically involves good hygiene, avoiding irritants, and using warm compresses or saline soaks. Keloids may be treated with corticosteroid injections, silicone sheets, cryotherapy, or surgery, although no definitive treatment works for everyone.
Remember, if you’re unsure whether you have a piercing bump or a keloid, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional or a licensed piercer for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention Tips
If you’re considering getting a piercing, there are a few things you can do to reduce your risk of developing a piercing bump or keloid scar. Here are some tips to help prevent these types of scars:
- Choose a reputable piercer: Make sure your piercer has experience and uses sterile equipment to reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid touching your piercing: Touching your piercing with dirty hands can introduce bacteria and irritate the skin.
- Keep your piercing clean: Follow your piercer’s aftercare instructions and clean your piercing regularly to reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid changing your jewelry too soon: Changing your jewelry too soon can irritate the piercing and increase your risk of developing a scar.
- Avoid tight clothing: Tight clothing can rub against the piercing and irritate the skin, increasing your risk of developing a bump or keloid.
- Avoid sleeping on your piercing: Sleeping on your piercing can pressure the skin and increase your risk of developing a scar.
- Avoid harsh products: Avoid using harsh products like alcohol or hydrogen peroxide to clean your piercing, as these can irritate the skin and increase your risk of developing a scar.
Following these tips can reduce your risk of developing a piercing bump or keloid scar. However, it’s important to remember that some people are more prone to developing these types of scars than others, and there’s no guaranteed way to prevent them entirely. If you develop a bump or keloid, talk to your piercer or a dermatologist for advice on treating it.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice a bump or scar developing around your piercing, it is important to keep an eye on it and monitor any changes. While most piercing bumps will go away with proper care and time, there are some situations where you should seek medical attention.
Here are some signs that you should seek medical attention:
- The bump is growing rapidly and is painful.
- The bump is hot to the touch or has pus coming out of it.
- The bump is not going away after several weeks of proper care.
- You notice any signs of infection, such as fever or chills.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking medical attention as soon as possible is important. A medical professional can help determine if the bump is a keloid or another type of infection and provide proper treatment.
It is also important to seek medical attention if you have a history of keloids or hypertrophic scarring. Your doctor may recommend avoiding certain types of piercings or using special techniques to reduce the risk of scarring.
Remember, it is always better to err on caution regarding your health. Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you have any concerns about your piercing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I differentiate between a piercing bump and a keloid?
Piercing bumps and keloids can look similar, but some key differences exist. Piercing bumps are usually smaller and may appear as a white or red bump around the piercing site. They can be itchy or painful and may contain pus. Keloids are larger and can be raised, thick, and dark in color. They may also extend beyond the piercing site and grow over time.
What are the treatment options for piercing bumps and keloids?
Treatment options for piercing bumps and keloids may include topical treatments such as tea tree oil or hydrocortisone cream and oral medications such as antibiotics or steroids. In some cases, surgical removal or laser therapy may be necessary. Consulting with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is important.
Can accidentally popping a piercing bump lead to keloid formation?
Accidentally popping a piercing bump can lead to further irritation and inflammation, which may increase the risk of keloid formation. It is important to avoid touching or picking at the bump and to follow proper aftercare instructions provided by your piercer.
Will removing the piercing make the bump go away?
Removing the piercing may help reduce irritation and inflammation, but it may not make the bump disappear. Sometimes, scar tissue may form even after the piercing is removed. Consulting with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is important.
Do all piercing bumps eventually turn into keloids?
No, not all piercing bumps will turn into keloids. Various factors, including infection or trauma to the piercing site, can cause piercing bumps. Keloids are a specific type of scar that may occur in some individuals prone to excessive scarring.
Are there any preventative measures to avoid developing piercing bumps or keloids?
To reduce the risk of developing piercing bumps or keloids, it is important to follow proper aftercare instructions provided by your piercer. This may include cleaning the piercing site regularly, avoiding touching or picking at the piercing, and avoiding tight clothing or jewelry that may irritate. If you are prone to keloid formation, avoid getting piercings altogether.
Conclusion
In conclusion about Piercing Bump vs Keloid, it is important to understand the difference between a piercing bump and a keloid. Piercing bumps tend to appear soon after a piercing and are temporary areas of swelling. They do not grow in size and may disappear independently without treatment. On the other hand, keloids are permanent bumps that can develop from any scar, including a piercing wound. They tend to be darker in color and can grow beyond the boundaries of the original wound.
If you have a piercing bump, keeping the area clean and avoiding touching or picking at it is important. A warm compress or sea salt solution may help reduce inflammation and promote healing. If the bump persists or becomes painful, consult a professional piercer or dermatologist for further advice.
If you suspect you have a keloid, it is important to seek medical attention. Treatment options may include corticosteroid injections, cryotherapy, or surgical removal. However, it is important to note that keloids tend to recur even after treatment.
Remember, everyone’s body is different, and there is no guarantee that you will not develop a Piercing Bump vs Keloid. However, taking proper care of your piercing and seeking medical attention when necessary can reduce your risk of complications and promote healing.
Also Read:
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy of Person with PAD