Stress is a common experience that everyone encounters in their daily life. It can be caused by various factors such as work, relationships, health, and financial issues. Stress can affect your physical and mental health in many ways, and one of the most commonly affected systems is your respiratory system.
Your respiratory system is responsible for breathing and supplying oxygen to your body. When you experience stress, your body releases stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause your heart rate and blood pressure to increase, which can make it harder for you to breathe.
In this article, we will explore how stress affects your respiratory system and the potential consequences of chronic stress on your lung health. We will look at the physiological changes in your body when you experience stress and how they can impact your breathing. Additionally, we will provide tips on managing stress to reduce its adverse effects on your respiratory system.
The Respiratory System
Stress can affect your respiratory system, responsible for breathing and delivering oxygen to your body’s cells. The respiratory system consists of several organs and tissues that work together to provide oxygen to your body and remove carbon dioxide.
The Anatomy of the Respiratory System
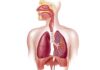
The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The nose and mouth are the entry points for air, passing through the throat and larynx before entering the trachea. The trachea then splits into two bronchi, which lead to the lungs. The lungs comprise tiny air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
The respiratory system is lined with tiny hairs called cilia, which help to filter out harmful particles and keep the airways clear. The system also produces mucus, which helps to trap bacteria and other toxic substances.
The Function of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system’s primary function is to provide oxygen to the body’s cells and remove carbon dioxide. When you inhale, oxygen enters your body and is carried by the bloodstream to your cells. When you exhale, carbon dioxide is removed from your body.
Stress can affect the respiratory system by causing changes in your breathing patterns. When you are stressed, your body may go into “fight or flight” mode, which can cause your breathing to become faster and shallower. This can lead to shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and chest tightness.
In addition, stress can cause the airway between the nose and lungs to constrict, making it harder to breathe. This can lead to symptoms such as wheezing and coughing. Chronic stress can also weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the respiratory system to fight off infections.
It is essential to manage stress to keep your respiratory system healthy. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help to reduce stress and improve respiratory function.
Stress and Its Effects on the Respiratory System
Stress can significantly impact your respiratory system, affecting your breathing and making it difficult to get the oxygen your body needs. The physiological stress response can trigger a range of symptoms affecting your respiratory system, including shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and chest tightness. In this section, we’ll explore the physiological response to stress and the impact of stress on the respiratory system.
The Physiological Response to Stress
When you experience stress, your body naturally releases stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones trigger a “fight or flight” response, which prepares your body to respond to a perceived threat. This response can cause your heart rate and breathing to increase and can also cause your muscles to tense up.
The physiological stress response can also cause your blood vessels to constrict, which can make it harder for oxygen to reach your lungs. As a result, you may experience shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. In addition, stress can cause inflammation in the airways, further exacerbating breathing difficulties.
The Impact of Stress on the Respiratory System
Stress can have a range of adverse effects on your respiratory system, including:
- Increased breathing rate: When you’re stressed, your breathing rate can increase, which can cause you to feel short of breath or lightheaded.
- Asthma symptoms: Stress can trigger asthma symptoms, such as wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Stress can worsen COPD symptoms, including shortness of breath and coughing.
- Sleep apnea: Stress can cause sleep disturbances, worsening sleep apnea symptoms.
Stress can worsen your symptoms if you have a pre-existing respiratory condition, such as asthma or COPD. It’s essential to manage your stress levels and seek treatment for your respiratory disease to prevent further complications.
Symptoms of Respiratory Problems Caused by Stress
Stress can cause various respiratory problems that can affect your breathing and overall health. Here are some of the most common symptoms of respiratory problems caused by stress:
Shortness of Breath
One of the most common symptoms of respiratory problems caused by stress is shortness of breath. When stressed, your body goes into fight or flight mode, and your breathing can become rapid and shallow. This can make it challenging to get enough air, which can cause you to feel like you’re not getting enough oxygen. Shortness of breath can be uncomfortable and even scary, but it’s usually not dangerous.
Chest Pain
Stress can also cause chest pain, which can be a symptom of a respiratory problem. When you’re stressed, your muscles can become tense, including the muscles in your chest. This can cause pain or discomfort in your chest, which can make it difficult to breathe deeply. Chest pain can signify a more serious respiratory problem, so it’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience it.
Wheezing
Wheezing is another common symptom of respiratory problems caused by stress. When you’re stressed, your airways can become inflamed, which can make it difficult to breathe. This inflammation can cause a whistling or wheezing sound when you breathe, which can indicate a respiratory problem. Wheezing can be uncomfortable and make it difficult to get enough air, so it’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience it.
Coughing
Coughing is another symptom of respiratory problems caused by stress. When you’re stressed, your body produces more mucus, which can cause you to cough. This can indicate a respiratory problem, especially if you’re coughing up phlegm or experiencing other symptoms like shortness of breath or wheezing. Coughing can be uncomfortable and make breathing difficult, so it’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience it.
Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Problems Caused by Stress
Stress can significantly impact your respiratory system, leading to respiratory problems like hyperventilation, shortness of breath, and respiratory alkalosis. Fortunately, there are several ways to prevent and treat these problems.
Stress Management Techniques
The first step in preventing respiratory problems caused by stress is to manage your stress levels. There are several stress management techniques that you can try:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Yoga and stretching
- Regular exercise
- Getting enough sleep
- Relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation or visualization
By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can reduce your overall stress levels and minimize stress’s impact on your respiratory system.
Medical Treatment
If you are experiencing respiratory problems caused by stress, there are medical treatments that can help. Your doctor may recommend the following:
- Oxygen therapy to increase your oxygen levels
- Breathing exercises to help you control your breathing
- Medications to help you relax and reduce anxiety
- Counseling or treatment to help you manage your stress levels
It is essential to seek medical treatment if you are experiencing respiratory problems, as they can have severe consequences if left untreated.
In addition to these treatments, it is vital to make lifestyle changes to reduce stress levels and prevent respiratory problems. This may include getting regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and getting enough sleep.
In conclusion, stress can significantly impact your respiratory system, leading to respiratory problems like hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. However, practicing stress management techniques and seeking medical treatment when necessary can prevent and treat these problems and maintain a healthy respiratory system.
Also Read:
Which Of The Following is Not a Function Of The Respiratory System