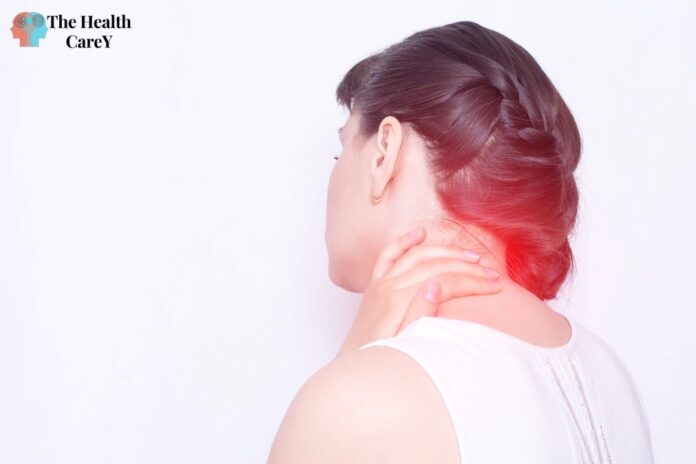
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with fibromyalgia, you may be wondering what exactly it is and whether it’s an autoimmune disease. Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder that causes widespread pain and tenderness throughout the body, as well as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and other symptoms. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, there is evidence to suggest that it may be related to the immune system.
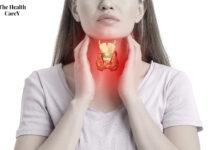
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body, causing inflammation and damage. Some examples of autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. While fibromyalgia is not typically classified as an autoimmune disease, there is growing evidence to suggest that it may involve immune dysfunction and inflammation. In fact, some researchers have proposed that fibromyalgia may be a subtype of autoimmune disease or a related condition.
Is Fibromyalgia an Autoimmune Disease?
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with fibromyalgia, you may be wondering if it is an autoimmune disease. While fibromyalgia is not classified as an autoimmune disease, there is evidence to suggest that it may involve an autoimmune component.
Definition and Symptoms
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and tenderness in the muscles and soft tissues. Other symptoms may include sleep disturbances, headaches, irritable bowel syndrome, and cognitive difficulties.
Pathophysiology
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not yet fully understood. However, research suggests that it may involve dysregulation of the immune system. Studies have shown that people with fibromyalgia have higher levels of inflammatory markers in their blood, which suggests that inflammation may play a role in the development of the condition.
Additionally, some researchers believe that fibromyalgia may involve an autoimmune component. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body. While fibromyalgia is not considered an autoimmune disease, some studies have found that people with fibromyalgia have higher levels of autoantibodies, which are antibodies that target the body’s own tissues.
In conclusion, while fibromyalgia is not classified as an autoimmune disease, there is evidence to suggest that it may involve dysregulation of the immune system and an autoimmune component. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between fibromyalgia and the immune system.
Autoimmune Disease Overview
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body. This can lead to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and a range of symptoms that vary depending on the specific disorder.
Characteristics of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the presence of autoantibodies, which are antibodies that target the body’s own tissues. These autoantibodies can cause damage to various organs and tissues, leading to a range of symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, rashes, and digestive problems.
Another hallmark of autoimmune diseases is chronic inflammation, which can lead to tissue damage and scarring over time. In some cases, autoimmune diseases can also increase the risk of other health problems such as infections, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Common Autoimmune Disorders
There are more than 80 different autoimmune disorders that have been identified, with varying degrees of severity and symptoms. Some of the most common autoimmune disorders include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Multiple sclerosis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Crohn’s disease
- Psoriasis
While the exact cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment typically involves managing symptoms and reducing inflammation through medication, lifestyle changes, and other therapies.
Investigating the Link between Fibromyalgia and Autoimmune Disease

Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, researchers have been investigating the link between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases.
Research on Fibromyalgia and Immunity
Research has shown that people with fibromyalgia may have an overactive immune system. This means that the immune system may be attacking healthy cells and tissues in the body, leading to inflammation and pain. Some studies have also suggested that fibromyalgia may be linked to specific autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
However, other studies have not found a clear link between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases. More research is needed to fully understand the relationship between fibromyalgia and immunity.
Comparative Analysis
To better understand the potential link between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases, researchers have conducted comparative analyses. These analyses compare the immune system activity of people with fibromyalgia to those with autoimmune diseases and healthy individuals.
One comparative analysis found that people with fibromyalgia had similar immune system activity to those with autoimmune diseases, but different from healthy individuals. This suggests that there may be some shared immune system dysfunction between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases.
However, other comparative analyses have found no significant differences in immune system activity between people with fibromyalgia and healthy individuals. It is important to note that comparative analyses have limitations and may not fully capture the complexity of immune system activity.
Overall, while there is some evidence to suggest a potential link between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether fibromyalgia is an autoimmune disease remains a topic of debate among medical professionals. While some evidence suggests that fibromyalgia may have autoimmune components, such as the presence of autoantibodies and the association with other autoimmune diseases, the exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unknown.
It is important to note that fibromyalgia is a complex condition that involves multiple factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and psychological factors. Therefore, it is unlikely that fibromyalgia can be attributed solely to an autoimmune mechanism.
Further research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms of fibromyalgia and to develop more effective treatments for this condition. In the meantime, individuals with fibromyalgia can benefit from a multidisciplinary approach to treatment that addresses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the latest research on fibromyalgia as of 2023?
Fibromyalgia is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. As of 2023, researchers continue to study the underlying causes and potential treatments for fibromyalgia. Recent studies have focused on the role of the immune system in fibromyalgia, as well as the potential benefits of exercise and cognitive behavioral therapy.
Can fibromyalgia be considered a chronic illness?
Yes, fibromyalgia is considered a chronic illness. It is characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and other symptoms that can last for months or even years. While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, there are treatments that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
What are the commonalities between fibromyalgia and inflammatory diseases?
Fibromyalgia shares some similarities with inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Both conditions can cause pain, fatigue, and other symptoms. However, fibromyalgia is not considered an inflammatory disease, as there is no evidence of inflammation in the muscles or joints of people with fibromyalgia.
Which autoimmune diseases are commonly associated with fibromyalgia?
There is some evidence to suggest that fibromyalgia may be more common in people with certain autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. However, the relationship between fibromyalgia and autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, and more research is needed to determine the exact nature of this connection.
How does fibromyalgia differ from neurological conditions?
Fibromyalgia is a condition that primarily affects the muscles and joints, while neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease affect the nervous system. While there may be some overlap in symptoms, such as fatigue and cognitive difficulties, the underlying causes and mechanisms of these conditions are different.
What are the implications of receiving a COVID vaccine for individuals with fibromyalgia?
As of 2023, there is no evidence to suggest that receiving a COVID vaccine would have any negative implications for individuals with fibromyalgia. In fact, getting vaccinated may help protect against COVID-19 and reduce the risk of complications from the virus.
Can COVID cause fibromyalgia?
There is currently no evidence to suggest that COVID-19 can cause fibromyalgia. However, some people with COVID-19 may experience symptoms similar to those of fibromyalgia, such as muscle pain and fatigue. More research is needed to determine the long-term effects of COVID-19 on the body and whether it can lead to the development of fibromyalgia.